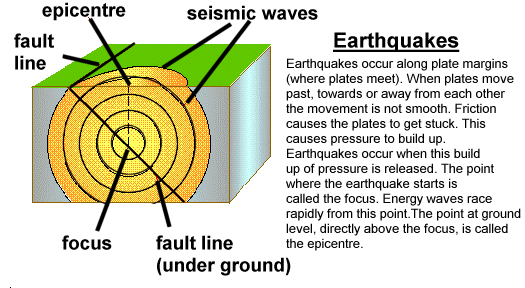
WELL THIS REMINDS ME OF THE QUOTATION THAT “NOTHING IS BEYOND MAN’S REACH”
NOT A JOKE BUT YES IT IS POSSIBLE TO CREATE YOUR OWN EARTHQUAKE ……BUT UNFORTUNATELY THIS IS NOT A MATTER OF BEING PROUD OF THE “TECHNICAL ACHIEVEMENT” BUT A MATTER OF IMMENSE “SHAME” FOR THE ENTIRE HUMANITY…
Here is a list of “human efforts” to call the “death”
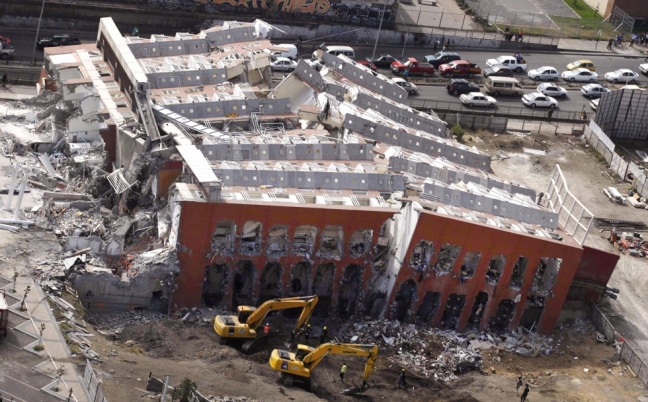
2008 Sichuan, China earthquake
It’s just water, but, man, water is heavy. Large reservoirs of water created by dams have a long history of inducing earthquakes, from Zambia to Greece to India. The 2008 earthquake in Sichuan, China, that killed nearly 70,000 people was one of the most devastating in recent memory, and some scientists think it was triggered by the construction of the Zipingpu Dam nearby.
The Zipingpu Dam sits just a third of a mile away from the fault, and the added weight of millions of tons of water could have hastened the fault’s rupture. “No geological process can come up with such a concentration of mass in such as small area other than a volcano,” said geologist Christian Klose about the buildup of water.
Groundwater extraction — 2011 Lorca earthquake
Taking water out of ground, which causes the water table to drop, can also destabilize an existing fault.
A 2011 earthquake in Lorca, Spain caused a great amount of destruction for its 5.1 magnitude because its epicenter was located so close to the surface. Its shallow epicenter may be related to groundwater extraction near Lorca, according to research published in Nature Geoscience. Since 1960, water extraction has caused the region’s water table to drop by an incredible 250 meters.
Geothermal power plants — Salton Sea Geothermal Field and The Geyers Geothermal Field

At the end of the infamous San Andreas Fault in California lies the Salton Sea—and, along its southern shore, is the Salton Sea Geothermal Field. The power plant extracts hot, high-pressured water out of the ground and turns it into steam to run turbines generating power. If it seems like a bad idea to be extracting water so close to the San Andreas Fault, well, you’d be right.
In a 2011 study published in Science, researchers at the University of California, Santa Cruz, found that seismic activity has increased around the Salton Sea as geothermal field operations have ramped up. Earthquake swarms—bursts of dozens of small quakes below magnitude 6 or so—happen regularly along the Salton Sea. While these earthquake swarms by themselves may not cause much damage, they could interact with other bigger faults, like the San Andreas located so conveniently nearby, to induce far more damaging quakes.
Several hundred miles north in California is also the Geysers Geothermal Field, the largest geothermal field in the world. Because the Geysers don’t sit near a large fault, induced seismicity there is less likely to be majorly destructive. However, researchers have found that seismicity in the region has increased from basically zero in the 1960s to 20 or 30 small seismic events per year.
Fracking and injection wells — 2011 Oklahoma earthquake
When it comes to hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, it’s actually not the extraction of oil or gas that’s the problem. . It’s what happens to those afterward, when waste fracking fluid is injected back underground into deep wells. The fluid can seep out and lubricate faults, causing them to slip more easily. A study in Geology links a 2011 Oklahoma earthquake to wastewaterinjection wells.
Seismic activity in Oklahoma has shot up along with the rise of fracking: The number of earthquakes went from about a dozen in 2008 to over 1,000 in 2010. Earthquake swarms are now regular occurrences in the region. With fracking in the United States steadily increasing, the dangers of wastewater injection wells become more imminent.
Skyscrapers — Taipei 101

The tallest building in the world when it was built, the Taipei 101 tower in Taiwan was supposed to be the city’s crown jewel, capable of withstanding typhoon winds and earthquakes. Ironically, the very things supposed to make it earthquake-resilient may be… causing earthquakes.
According to a Taiwanese geologist Cheng-Horn Lin, Taipei 101’s especially huge mass of 770,000 tons is putting too much pressure on the soft sedimentary rock below. This stress is due to all the extra steel and concrete used to make the skyscraper solid enough to withstand earthquakes. Since construction began on Taipei 101, according to Lin, the region has seen several micro-earthquakes and two larger earthquakes directly underneath the building.
During its construction in March 2002, a 6.8 earthquake did knock two cranes to the ground. Taipei 101 itself, though, was undamaged. So, if the skyscraper does cause earthquakes in the future, at least you know where to go?
Overenthusiastic Sports Fans — Seahawks Game, Seattle
When the Seattle Seahawks scored a touchdown on a fumble return last week, the seismometer down the block was keeping score. The University of Washington’s seismometer just one block south of CenturyLink Field registered a magnitude 1 or 2 earthquake from the rumbling of Seahawks fans. When your seismometer is so close, though, does it even really count? Well, here’s an empowering message: Stand close enough to a seismometer and you, too, can cause your very own earthquake.